Complication Management
What can you do if a clip needs to be removed? In such cases, appropriate complication management is required.
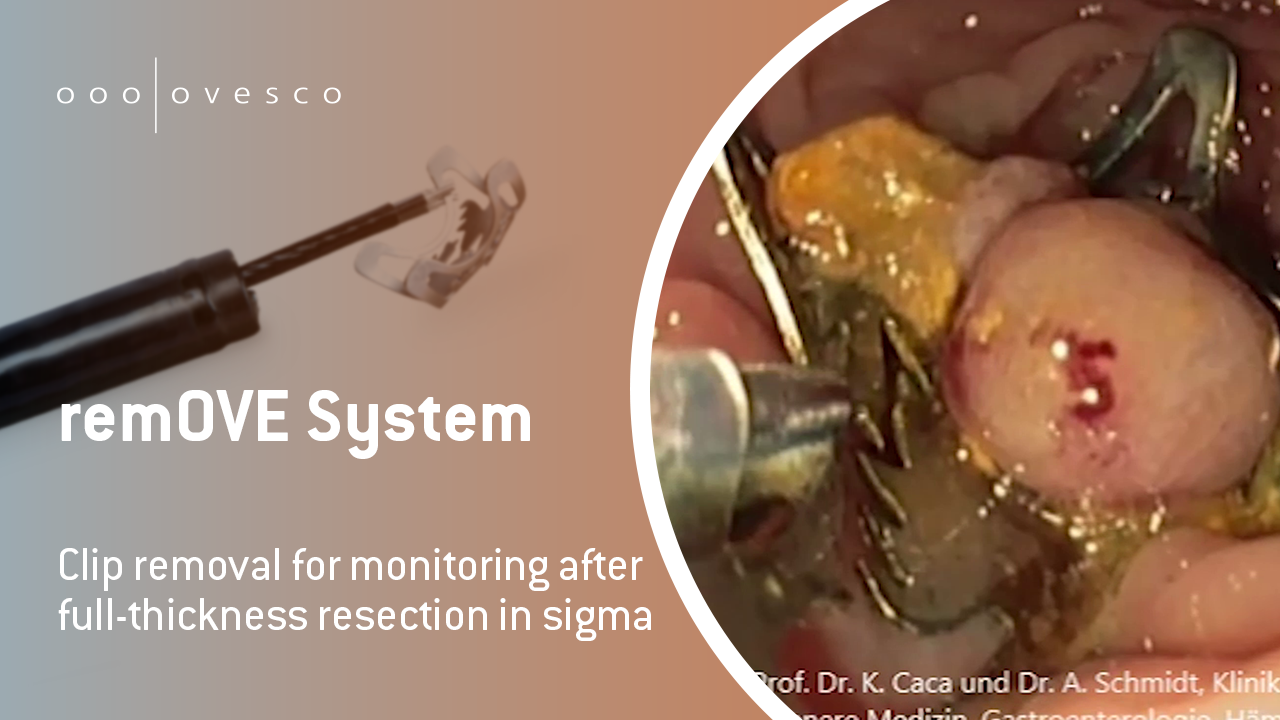
Ovesco clips are biocompatible and can remain in the body permanently. In most cases, they detach on their own after healing is complete and are excreted naturally. However, there are situations in which targeted removal of the clip may be necessary. Ovesco takes a multifaceted approach that goes beyond mere application and also includes complication management with the remOVE System.
Indications
A major challenge in stent placement is the subsequent risk of migration. With the stentFIX System, stents can be fixed distally and proximally to significantly reduce this risk. A specially designed Ovesco clip is used to fix the stent to the tissue. For subsequent removal of the stent, the fixing clip can be systematically fragmented and removed with the remOVE System.
In rare cases, a clip may be accidentally placed in an unintended location. Removal is then necessary to avoid complications and ensure correct therapy. The remOVE System provides the necessary safety during clip placement, especially for beginners.
In rare cases, during certain endoscopic procedures, an instrument may be accidentally clipped to the tissue. The remOVE System offers a reliable and gentle way to remove the clip, solving the problem quickly and reliably.
In rare cases, clip placement can lead to complications such as lumen narrowing, which may require removal of the clip.
For diagnostic purposes or repeat endoscopic therapy, it may be necessary to make the clip site accessible for biopsy or re-resection.
An MRI scan is necessary near the clip, but the clip may cause artifacts in the imaging. To prevent this, the clip can be removed with the remOVE System, enabling high-quality diagnostic imaging without interference.
Even though Ovesco clips can remain in the patient's body without any problems, there are cases where patients want to have the clips removed. With the remOVE System, this request can be fulfilled quickly and easily.
Procedure
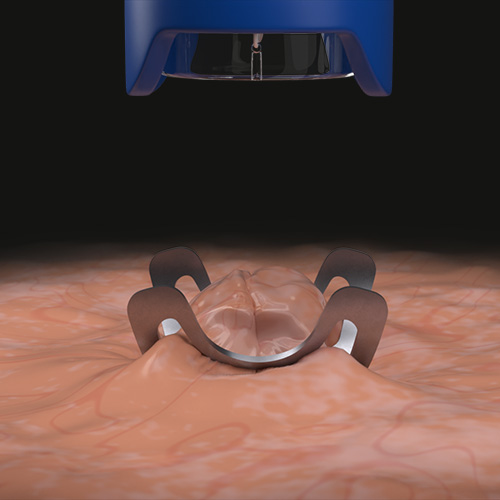
The remOVE System is the only system to easily remove clips from the gastrointestinal tract. It consists of various components, including the remOVE DC Impulse Generator, which generates a direct current impulse, the DC Cutter, which cuts the clip using direct current, and the SecureCap, which securely retrieves the clip fragments. For this purpose, the remOVE Grasper is used as a grasping instrument to secure the clip fragments in the SecureCap. The system also includes the remOVE Shield*, which protects the endoscope lens from flying sparks.
To remove the clip, the DC Cutter is inserted through the working channel and the clip is fragmented at two opposite points. The clip fragments are then mobilized into the SecureCap using the Grasper. This allows them to be retrieved while protecting the tissue at the same time.
*The remOVE Shield may not be available in all regions